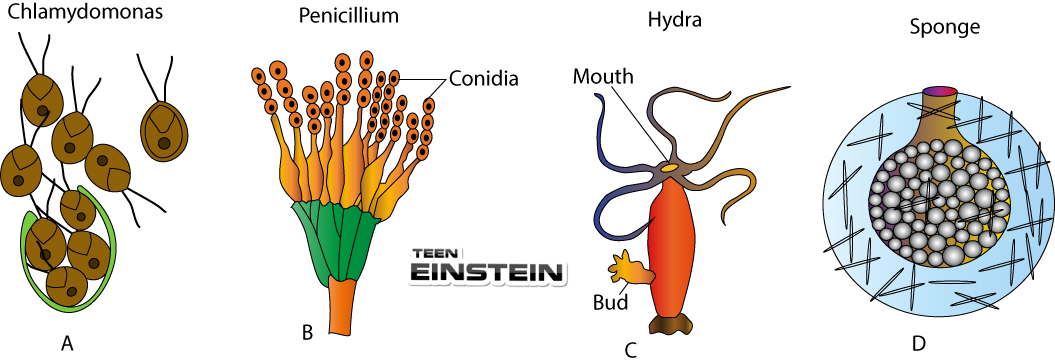
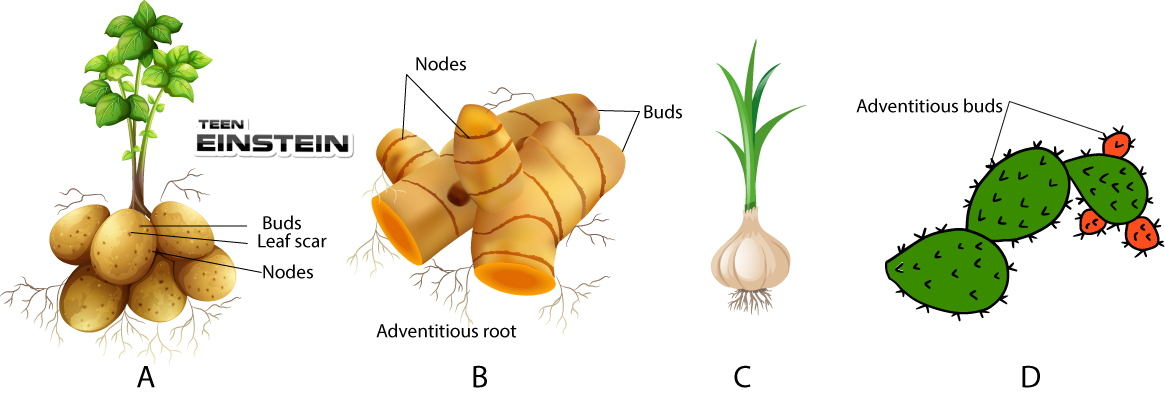
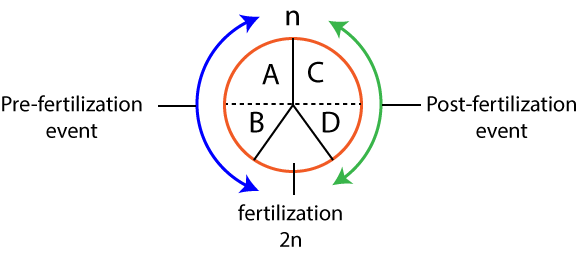
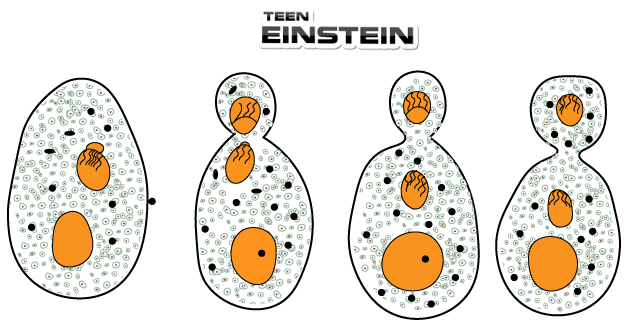
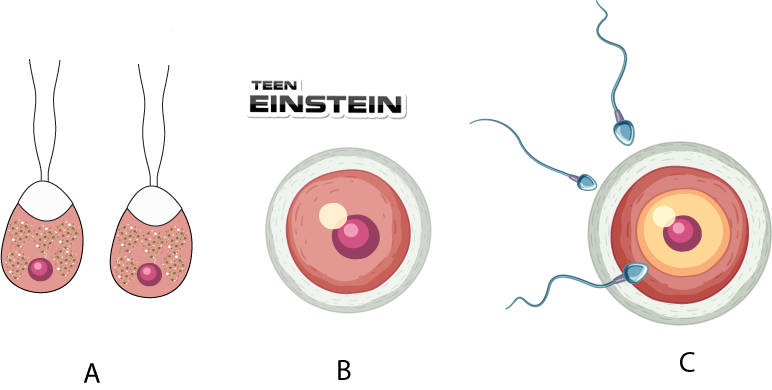
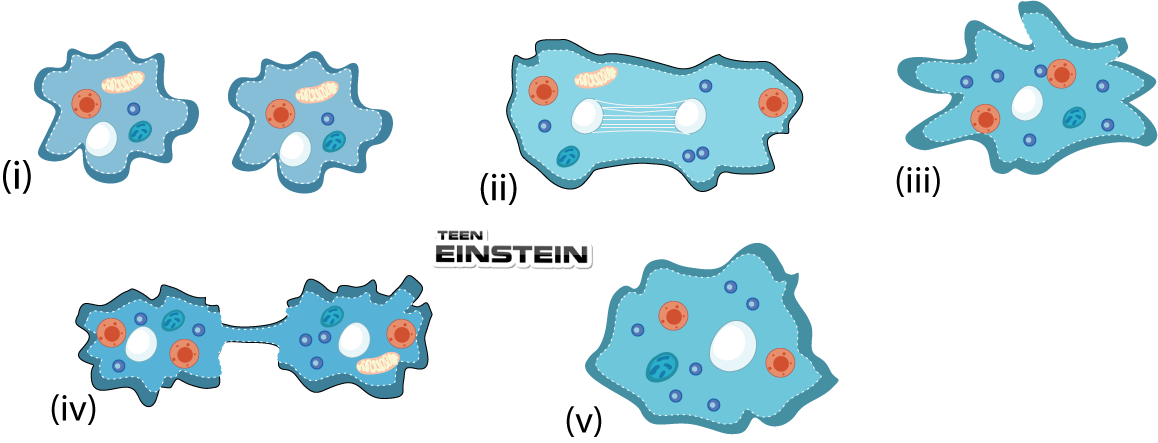
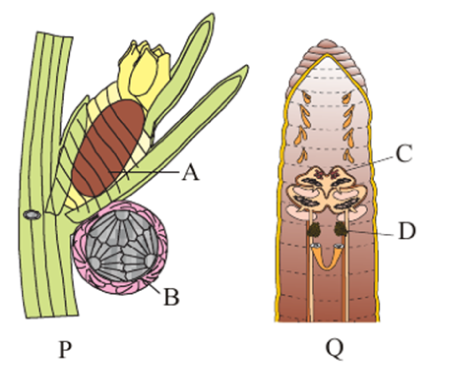
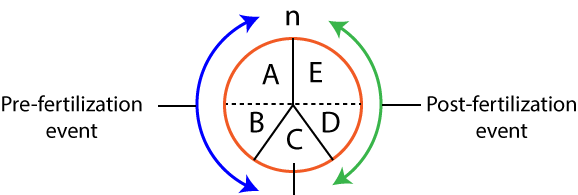
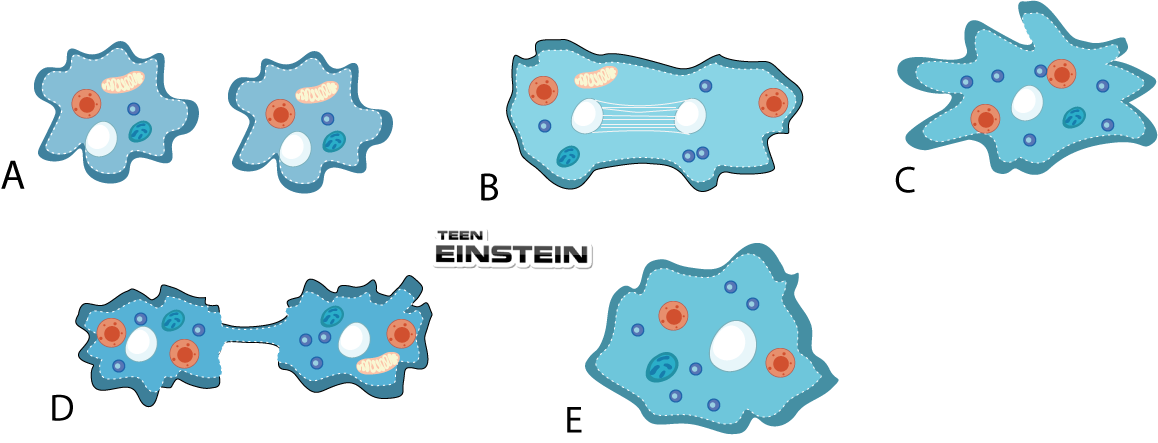
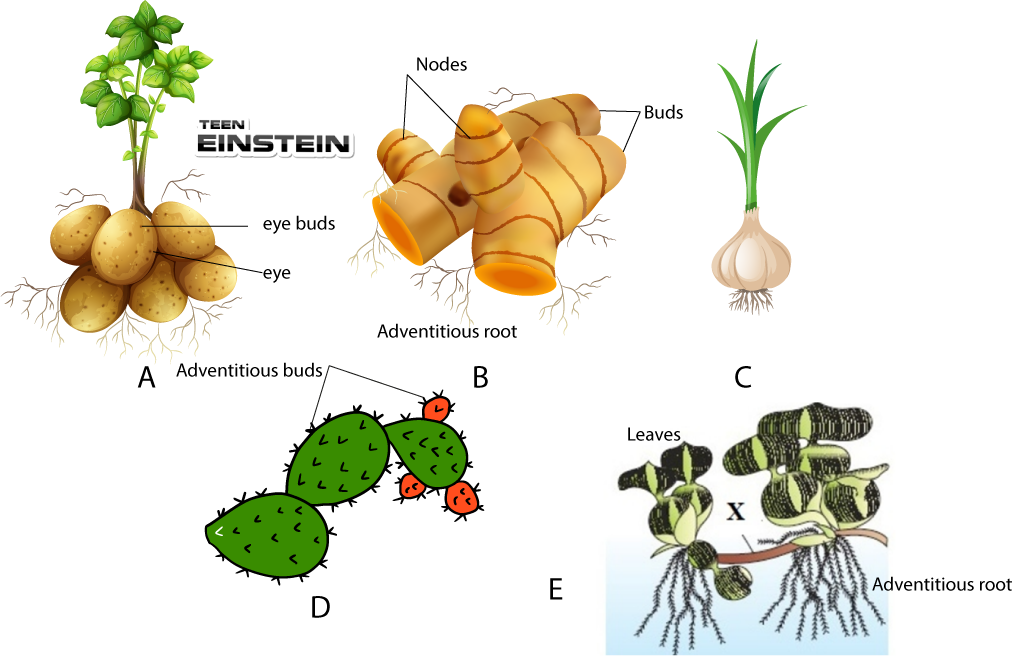
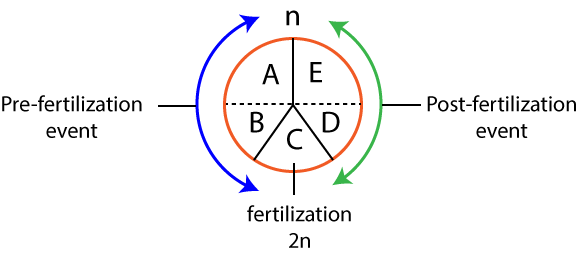
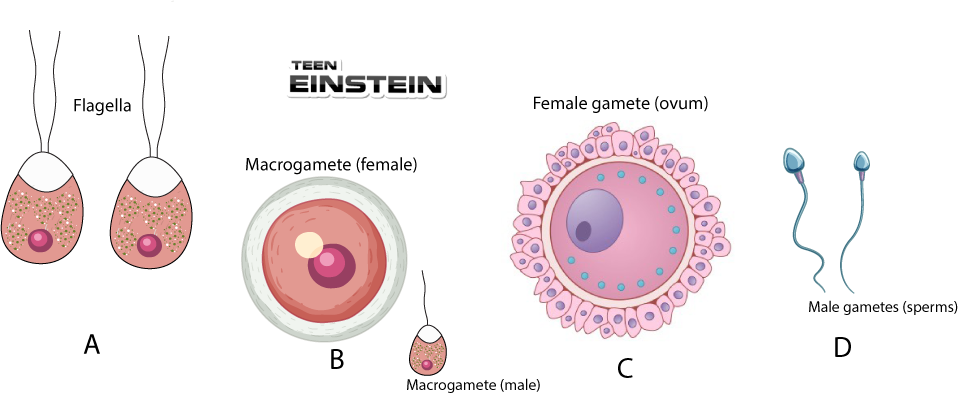
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Gamete | I. Result of fusion of male and female gametes |
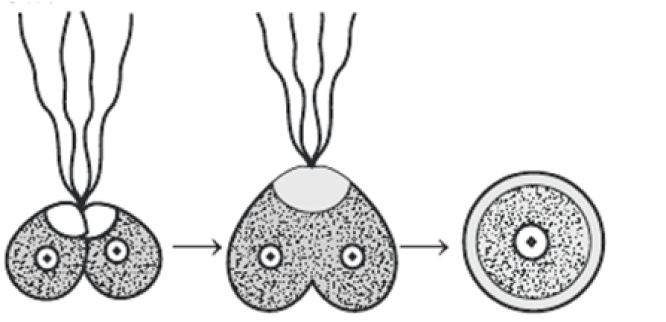
| B. Budding | II. Division of body into two equal halves |
| C. Fission | III. Germ cells |
| D. Fertilization | IV. The fusion of male and female gametes |
| E. Zygote | V. An unequal division of organisms in which individual arises as an outgrowth from the parent |